ELISA method to detect ABO blood group in external secretion fluids
Abstract
Background: Usually it takes a large number of volume sample to determine blood group from external secretion fluids. But, in certain condition, samples are only available in very small amount. The objective of this study is to detect the presence of ABO blood group substances in mucosal fluid using ELISA technique, thus only requires small amount of samples.
Objective: To develop an ELISA technique using the current anti-ABO antibodies for determination of blood group by hemagglutination technique and second peroxidase label antibody specific for mouse IgG, originally used for another ELISA technique.
Methods: 100 μl of diluted human intestinal mucosal fluid were incubated overnight in 4oC in ELISA microplate wells, followed by addition anti-ABO antibodies. Then after incubation, a second revealing antibody anti mouse IgG labeled with peroxidase was added. After a brief incubation, substrate H2O2 and chromogenic TMB were added.
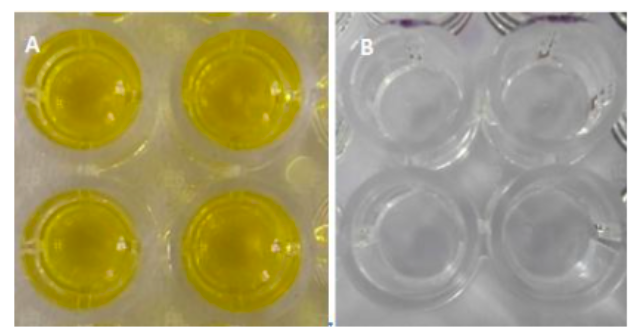
Results: Positive reaction is marked by development of blue colour, which, on termination enzymatic reaction by addition 100 μl H2SO4 change to yellow.
Conclusion: An ELISA method for detecting ABO substance in mucosal fluid can be developed from antibodies not specifically made for this technique, but specific only for the target.
References
Watkins W. The ABO blood group system: historical background. Transfusion medicine. 2001;11(4):243-265. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3148.2001.00321.x
Mohn J, Owens N, Plunkett R. The inhibitory properties of group A and B non-secretor saliva. Immunological communications. 1981;10(3):315-340. https://doi.org/10.3109/08820138109093464
Saboor M, Ullah A, Qamar K, Mir A, et al. Frequency of ABH secretors and non secretors: A cross sectional study in Karachi. Pakistan journal of medical sciences. 2014;30(1):189. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.301.4194
Metgud R, Khajuria N, Mamta GR. Evaluation of the secretor status of ABO blood group antigens in saliva among southern Rajasthan population using absorption inhibition method. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR. 2016;10(2):ZC01. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2016/11598.7161
Kind S. Absorption-elution grouping of dried blood smears. Nature. 1960;185(4710):397. https://doi.org/10.1038/185397b0
Boyd WC, Shapleigh E. Separation of individuals of any blood group into secretors and non-secretors by use of a plant agglutinin (lectin). Blood. 1954;9(12):1195-1198. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V9.12.1195.1195
Avrameas A. Methode de marquage d'antigen et danticorps avec des enzymes et son application en immunodiffusion. Cr Acad Sci, D. 1966;262:2543-2545.
Avrameas S, Guilbert B. A method for quantitative determination of cellular immunoglobulins by enzyme-labeled antibodies. European journal of immunology. 1971;1(5):394-396. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830010518
Van WB, Schuurs A. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS letters. 1971;15(3):232-236. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(71)80319-8
Engvall E, Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971;8(9):871-874. https://doi.org/10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-X
Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El GF, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Cogliano V. Carcinogenic of some aromatic amines, organic dyes, and related exposure. The Lancet Oncology. 2009;9(4):322-323 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70089-5
Chung KT, Chen SC, Wong TY, Li YS, Wei CL, Chou MW. Mutagenicity studies of benzidine and its analogs: Structure-Activity Relationship. Toxicological Sciences. 2000;56(2):351-356 https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/56.2.351
Holland VR, Saunders BC, Rose FL, Walpole AL. A safer subsititute for benzidine in the detection of blood. Tetrahedron. 1974;30(18):3299-3302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97504-0
Watkins WM. Genetic and biochemistry of some human blood groups. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B. Biological Sciences. 1978;202(1146):31-35 https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1978.0056
Copyright (c) 2019 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







