Antibacterial activity of betel (Piper betle L.) fruit against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
Background: Betel (Piper betle L.) is a well-known medicinal plant for its numerous health benefits. Saponins, flavonoids, polyphenols, and essential oils are among the chemical constituents of betel plants. Flavonoids are one of the most common groups of secondary metabolites found in plant tissues, including in betel plants.
Objective: The purpose of this research is to isolate flavonoids from betel fruit and to determine the antibacterial activity of betel fruit extract against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Methods: Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) with the eluent chloroform: methanol: water was used to isolate flavonoids. UV-Vis spectrophotometry was used to determine the presence of flavonoids in betel fruit. The antibacterial activity of extract and TLC-isolates of betel fruit was tested by using the disc method.
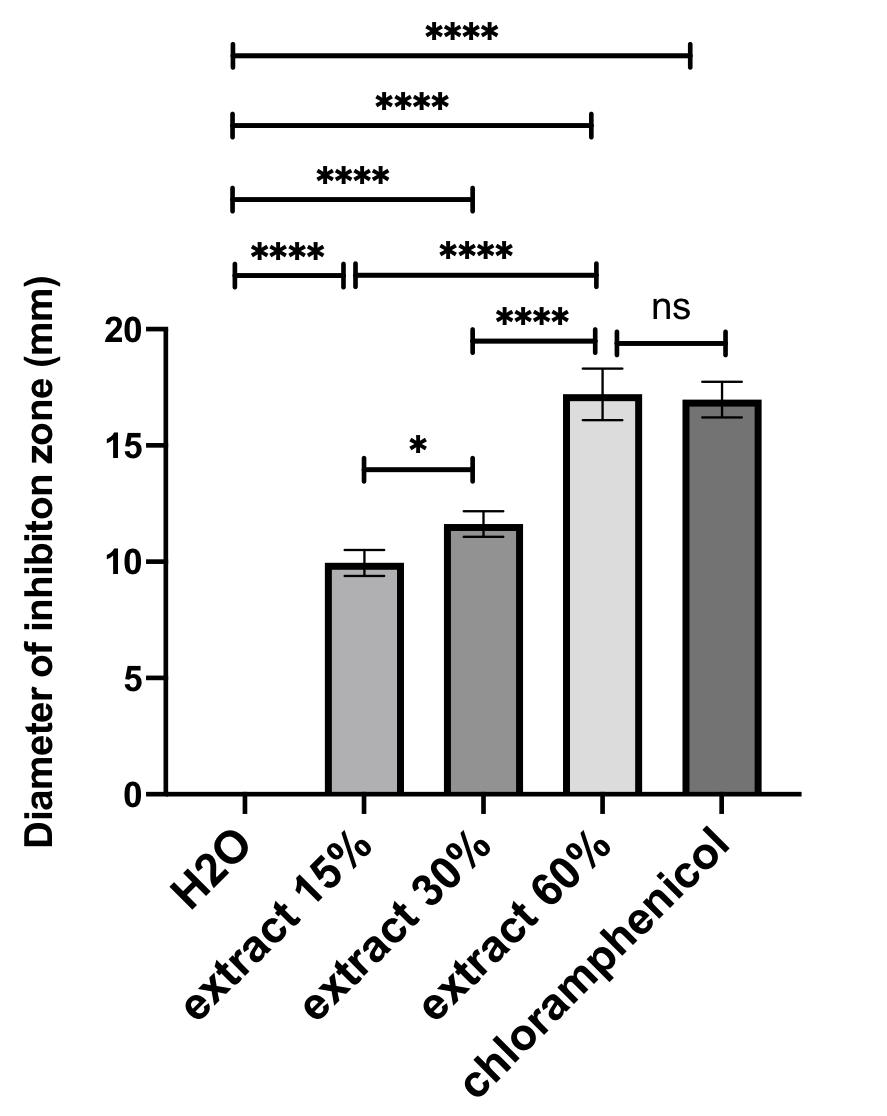
Results: TLC analysis resulted in the formation of a brown stain. The UV-Vis spectrophotometry results revealed two absorption bands at 366 nm and 268 nm, indicating that flavonoids are present in betel fruit. Antibacterial activity test against Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria showed that the concentration of 30% and 60% of betel fruit extract had strong antibacterial activity.
Conclusion: The results revealed that the betel fruit contains flavonoid compounds, and the extract has medium to strong antibacterial activity.
References
Pang Z, Raudonis R, Glick BR, Lin T-J, Cheng Z. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37: 177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013
Zar’ah NA, Syachruddin S, Kusmiyati K. The Effect of Green Betel Leaves (Piper betle L.) Extract on Wounding Healing in Mice (Mus musculus L.). JBT. 2021;21: 103. https://doi.org/10.29303/jbt.v21i1.2282
Lubis RR, Marlisa, Wahyuni DD. Antibacterial activity of betle leaf (Piper betle l.) extract on inhibiting Staphylococcus aureus in conjunctivitis patient. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2020;9: 1–5.
Ermawati FU, Sari R, Putri NP, Rohmawati L, Kusumawati DH, Munasir, et al. Antimicrobial activity analysis of Piper betle Linn leaves extract from Nganjuk, Sidoarjo and Batu against Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp., Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Phys: Conf Ser. 2021;1951: 012004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1951/1/012004
Dewi NLA. Pemisahan, Isolasi, dan Identifikasi Senyawa Saponin Dari Herba Pegagan (Centella asiatica L. Urban). jfu. 2018; 68. https://doi.org/10.24843/JFU.2018.v07.i02.p05
Ridwanuloh D, Syarif F. Isolasi dan Identifikasi Senyawa Flavonoid dari Batang Ciplukan (Physalis angulata L.). Pharma Xplore. 2019;4: 288–296. https://doi.org/10.36805/farmasi.v4i1.619
Jorgensen JH, Ferraro MJ. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: a review of general principles and contemporary practices. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49: 1749–1755. https://doi.org/10.1086/647952
Dewi NWRK, Gunawan IW, Puspawati NM. Isolasi dan Identifikasi Senyawa Antioksidan Golongan Flavonoid dari Ekstrak Etil Asetat Daun Pranijiwa (Euchresta horsfieldii Lesch Benn.). CK. 2017;5: 26. https://doi.org/10.24843/CK.2017.v05.i01.p04
Davis WW, Stout TR. Disc plate method of microbiological antibiotic assay. I. Factors influencing variability and error. Appl Microbiol. 1971;22: 659–665. https://doi.org/10.1128/am.22.4.659-665.1971
Yudha C, Karlina Y. Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Herba Krokot (Portulaca oleracea L.) terhadap Staphylococcus aureus dan Escherichia coli. LenteraBio: Berkala Ilmiah Biologi. 2013; 87–93.
Böttger S, Melzig MF. The influence of saponins on cell membrane cholesterol. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013;21: 7118–7124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2013.09.008
Makarewicz M, Drożdż I, Tarko T, Duda-Chodak A. The Interactions between Polyphenols and Microorganisms, Especially Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020188
Copyright (c) 2021 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







