Studies on biosurfactant produced using Exiguobacterium profundum
Abstract
Background: The manufacture of pharmaceutical preparations generally adds surfactants. Microbial biosurfactants can be an alternative because biodegradable and have antibacterial properties.
Objective: This study aimed to examine the biosurfactant activity of Exiguobacterium profundum.
Methods: Hemolysis and spreading oil tests were performed as an initial screening. Biosurfactant production was carried out by growing bacteria on oil-enriched media with shaker system for 7 days. Biosurfactant activity can be seen from the emulsification index, while the characterization of biosurfactant were used thin layer chromatography and antibacterial qualitative testing.
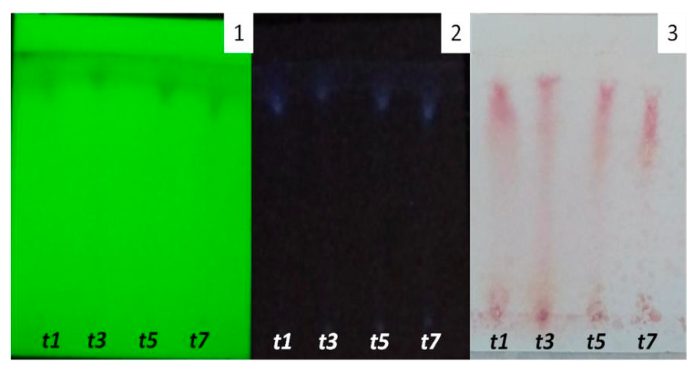
Results: Exiguobacterium profundum could spread the oil layer and form micelles. The emulsification index on days 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7 showed percentage in sequence 44.83%, 48.28%, 48.28%, 40%, and 43.75%. The result of TLC showed lipopeptide group which is marked with red stain with ninhydrin appearance. Antibacterial testing using Escherichia coli showed the formation of clear zones around the disk paper.
Conclusion: The biosurfactant produced by Exigoubacterium profundum can be classified into lipopeptide group which has antibacterial activity against gram-negative.
References
Reningtyas R., Mahreni M. Biosurfactant. Eksergi. 2015; 12(2) : 12-22. https://doi.org/10.31315/e.v12i2.1354
Riffiani R. Bakteri penghasil biosurfaktan yang diisolasi dari pulau laki kepulauan seribu. J. Hidrosfir Indonesia. 2010; 5(3) : 9-16
Fakruddin, Md. Biosurfactant: production and application. J Pet Env Biotechnol. 2012; 3(4) :1-5.
Ciccyliona DY, Nawfa R. Pengaruh pH terhadap produksi biosurfaktan oleh bakteri Pseudomonas aeruginosa lokal. J. Sains Dan Seni Pomits. 2012; 1(1) : 1-6.
Kasana RC, Pandey CB. (Review) Exiguobacterium: an overview of a versatile genus with potential in industry and agriculture. Journal Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 2018; 38(1) : 141-156. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2017.1312273
Sari M, Afiati F, Kusharyoto W. Potency of oil sludge bacteria as a producer of biosurfactant and antimicrobial agents. Pros. Semin. Nas. Masy. Biodiversitas Indones. 2015; 1(1): 85-88.
Saravanan V, Vijayakumar S. 2012. Isolation and screening of biosurfactant producing microorganisms from oil contaminated soil. J Acad Indus Res. 2012; 1(1) : 264-268.
Wewengkang DS, Sumilat DA, Rotinsulu H. Karakterisasi dan bioaktif antibakteri senyawa spons Haliclona sp. dari teluk Manado. J. LPPM Bid. SAINS DAN Teknol. 2014; 1(1): 71-85.
Techaoei S, Lumyong S, Prathumpai W, Santiarwarn D and Leelapornpisid P. Screening characterization and stability of biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa SCMU106 isolated from soil in Northern Thailand. Asian Journal of Biological Sciences. 2011; 4(4): 340-351. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajbs.2011.340.351
Gozan M, Fatimah IN, Nanda C, Haris A. Produksi biosurfaktan oleh Pseudomonas aeruginosa dengan substrat limbah biodiesel terozonasi untuk peningkatan. War. Ind. Has. Pertan. 2014; 31(2): 39-44.
Kurniati TH. Bakteri penghasil biosurfaktan dari lingkungan tercemar limbah minyak dan potensinya dalam mendegradasi Hidrokarbon Aromatik Polisiklik (HAP). [Skripsi]. Bogor: Institut Pertanian Bogor, 2016.
Kalyani R, Bishwambhar M, and Suneetha V. Recent potential usage of surfactant from microbial origin in pharmaceutical and biomedical arena : a perspective. International Research Journal of Pharmacy. 2011; 2(8) : 11-15.
Kubicki S, Bollinger A, Katzke N, Jaeger KE, Loeschcke A, and Thies S. Marine biosurfactants: biosynthesis, structural diversity and biotechnological applications. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(408) : 1-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070408
Das P, Mukherjee S, Sen R. Substrate dependent production of extracellular biosurfactant by a marine bacterium, Bioresour. Technol. 2009; 100(2) : 1015-1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.015
Harshada K. Biosurfactant: A potent antimicrobial agent, J Microbiol Exp. 2014; 1(5):173-177. https://doi.org/10.15406/jmen.2014.01.00031
Copyright (c) 2019 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







