Effectiveness of crude oil degrading fungi isolated from petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil in Siak, Riau
Abstract
Background: Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbon needs a specific technique called bioremediation to remove the environmental pollutants. Several indigenous microorganisms including fungi, bacteria, and actinomycetes are effective agents in degrading petroleum derivatives, aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
Objective: This research aimed to investigate indigenous fungi isolates from petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil in Siak which are capable to degrade hydrocarbon.
Methods: The competence of indigenous fungi was isolated from a crude oil-contaminated soil which collected from one of oil-field in Siak, Riau. The effectiveness of isolates on the degradation crude oil was tested by culturing the isolates in Bushnell-Haas broth containing crude oil (5% v/v) for 16 days. A decrease in pH, change in optical density and amount of CO2 released were recorded to indirectly indicate the crude oil degradation by the fungi. To measure the percentage of crude oil biodegradation, gravimetric analysis was utilized.
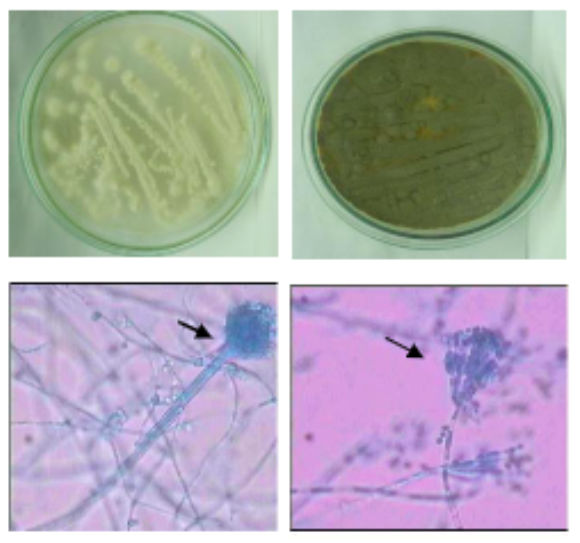
Results: The two colonies were selected and identified as Aspergillus sp LBKURCC151 and Penicillium sp LBKURCC153. The results showed that Aspergillus sp LBKURCC151 reached a higher level (61%) of biodegradation after 16 days under the optimum conditions in degrading total petroleum hydrocarbon than Penicillium sp LBKURCC153 (46%).
Conclusion: These results indicated that Aspergillus sp LBKURCC151 and Penicillium sp LBKURCC153 are potential degraders for bioremediation in crude oil-contaminated area.
References
Khan A, Tanveer S, Anees M, Muhammad YS, Iqbal M, Yousaf S. Role of nutrients and iilluminance in predicting the fate of fungal mediated petroleum hydrocarbon degradation and biomass production. Journal of Environmental Management. 2016;176:54-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.03.040
Bovio E, Gnavi G, Prigione V, Spina F, Denora R, Yakimov M, Varese GC. The culturable mycobiota of a Mediterranean marine site after an oil spill: Isolation, identification and potential application in bioremediation. Science of The Total Environment. 2017;576:310-318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.064
Napoleon A, Probowati DS. Exploration of hydrocarbon degrading bacteria on soils contaminated by crude oil from south sumatra. Journal of Degraded and Minning Lands Management. 2014; 201-206.
Al-Jawhari IF. Ability of some fungi isolated from a sediment of suq-al shuyukh marshes on biodegradation of crude oil. Int J. Curr. Microbiol. App.Sci. 2015;4(1):19-32.
Sudrajat D, Mulyana N, and Tri Retno DL. Isolasi dan aplikasi mikroba indigen pendegradasi hidrokarbon dari tanah tercemar minyak bumi. Prosiding pertemuan dan Presentasi Ilmiah-BATAN. 2015.
Maddela NR, Scalvenzi L, Perez M, Montero C, Gooty JM. Efficiency of indigenous filamentous fungi for biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in medium and soil: laboratory study from Ecuador. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2015;95:385-394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1605-6
Al-Nasrawi H. Biodegradation of crude oil by fungi isolated from gulf of mexico. J. Bioremediation & Biodegradation. 2012; 3:4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000147
Gilman JC, Joseph C. A Manual of soil fungi. Daya Publishing House. 1998.
Vanishree M, Thatheyus AJ, Ramya D. Biodegradation of petrol using the fungus penicillium sp. Science international. 2014;2(1):26-31. https://doi.org/10.17311/sciintl.2014.26.31
United states Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 1664 for extraction and gravimetric. Office of water, Washington DC, USA. 1999.
Burghal AA, Abu Mejdad NMJA, Al Tamimi WH. Mycodegradation of crude oil by fungal species isolated from petroleum contaminated soil. International journal of innovative research in science. Engineering and Technology. 2016;5:1517-1524.
Hussaini A, Roslan HA, Hii KSY, Ang CH. Biodegradation of aliphatic hydrocarbon by indigenous fungi isolated from used motor oil contaminated sites. J. Microbial Biotechnol. 2008;24: 2789-2797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9806-3
Atlas RM. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiological reviews. 1981;45(1): 180-209. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.45.1.180-209.1981
Srivasta S, Thakur IS. Evolution of Bioremediation and detoxification potentiality of Aspergillus niger for removal of hexavalent chromium in soil microcosm. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006; 38:1904-1911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.12.016
Adeogun OO, Adekunle AA. Biodegradation of petroleum products using phylloplane fungi isolated from selected plants. Journal of Sci. Res. Dev. 2015;15:45-53.
Dhar K, Anwar MN. Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbon by indigenous fungi isolated from ship breaking yards of bangladesh. International Research Journal of Biological Sciences. 2014; 22-30
Copyright (c) 2019 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







